Book Review by Somdatta Mandal

Title: Knife: Meditations After an Attempted Murder
Author: Salman Rushdie
Publisher: Penguin Random House
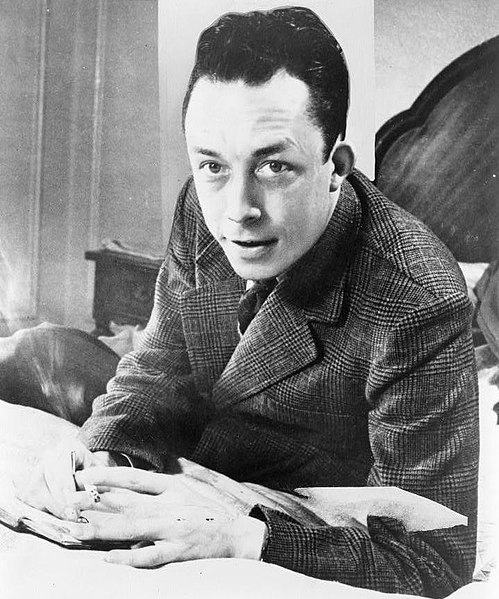
More than thirty years ago, a fatwa had been declared by Ayatollah Khomeini on the famous writer Salman Rushdie. The charge of blasphemy was labelled after the publication of The Satanic Verses, and since then the author has been living in asylum at different places because he was not safe in his own country. When it was assumed that the incident had died its natural death, the simmering vendetta and violence upsurged suddenly on 12th of August 2022, when Rushdie had gone to participate in a week of events at the Chautauqua Institution in upstate New York titled “More Than Shelter: Redefining the American Home”, and an unidentified man attempted to murder him on stage with a knife.
This horrific act of violence shook the entire world. No one hoped that they would ever be able to read a single line written by the author once again. He was a totally lost case. Now, one-and-a-half years after the incident, and in unforgettable detail, Rushdie writes this first-person memoir Knife where he relives the traumatic events of that day and its aftermath, as well as his journey towards physical recovery. His healing was made possible by the love and support of his present African American wife Eliza, his family, his army of doctors and physical therapists, and his readers worldwide.
Dedicating the book to the men and women who saved his life, the text is neatly divided into two parts, each containing four sections. The first half of the book titled “The Angel of Death” primarily revolves around ‘despair’, whereas the second part, “The Angel of Life,” narrates a vision of ‘hope’ and optimism and Rushdie’s attempt to return to normalcy once again with his indomitable spirit to fight on against all odds.
The opening chapter called ‘Knife’ begins with the description of a beautiful August morning in detail and how the apparent tranquility was shattered when suddenly violence appeared in the form of an unidentified man who rushed at him on the open stage and stabbed him indiscriminately. Totally flabbergasted, Rushdie obviously didn’t know what to do. So, he narrates the rest of the incidents in the form of a collage, with bits of memory pieced together with other eyewitness and news reports and tells us how that morning he “experienced both the worst and the best of human nature, almost simultaneously.” Though the incident of his attempted murder dragged “that” novel back into the narrative of scandal, Rushdie declares that till date he still felt proud of having written The Satanic Verses.
Apart from the day-by-day narration of how things shaped up after the stabbing incident, three things stand out very clearly in this memoir. First is of course the detailed description of his entire eighteen-day long stay initially at the extreme-trauma ward of the hospital and later at the rehab centre titled ‘Hamot’. Though in extreme pain we are told how doing a few simple everyday things for himself lifted his spirits greatly. So, apart from the rehab of the body, there was also the rehab of the mind and spirit. Spending more than six weeks in two hospitals, he could return to the world and so slowly he started feeling optimistic again.
The chapter called ‘Homecoming’ begins with his leaving the hospital at 3 A.M. as quietly as possible and going back home at that unearthly hour to evade any watching eyes.
Emotionally moved, even though he had lost one eye permanently, he felt “100 percent better and healthier immediately. I was home.”
The incident of homecoming is once again closely related to the second important issue during his convalescence –the love, care and bonding with his present wife Eliza. Dedicating a total chapter titled “Eliza”, Rushdie gives us details of how he met the African American poet Rachel Eliza Griffiths entirely unknown to him, through the eminent American writer, Norman Mailer, and how his friendship grew stronger day by day, leading to a secret marriage based on the realisation that it was a relationship not of competitiveness but of total mutual support. They showed that even in this attention-addicted time, it was still possible for two people to lead, pretty openly, a happily private life till the knife incident changed everything. He tells us how the poetical sensibilities of his wife lent extra support to him in such trying times.
The third most significant aspect of this memoir is the way Rushdie devotes an entire chapter addressed to his assassin –“The A”. And it is really at its imaginative best. In it he has recorded a detailed conversation that never actually occurred between himself and “a man I met for only twenty-seven seconds of my life”. After bringing in several intertextual references about other writers and situations, about other murders being committed in the lives of different personalities, in the fourth and final session of his imaginative conversation, Rushdie states, “You don’t know me. You’ll never know me.” After the imagined conversation is over, he no longer has the energy to imagine the assassin, just as he never had the ability to imagine him. He feels that the purgation is complete, and this chapter of his life is closed once and for all.
Interestingly after half a year of nothingness, Rushdie realises that his writing juices had indeed started to flow again. During his sleepless nights at the rehab, he often thought a lot about The Knife as an idea. Talking about different occasions and purposes when the knife is used, he realized that the knife is basically a tool and acquires meaning from the use we make of it. It is morally neutral, and it is the misuse of knives that is immoral. Then he states that language too was a knife for him, and he would use it to fight back. Here he made a resolution that instead of remaining as a mere victim, he would answer violence with art – “Hello, world, we were saying. We’re back, and after our encounter with hatred, we’re celebrating the survival of love. After the angel of death, the angel of life.” But it was hard for him to write about post-traumatic stress disorder at any time especially when his hand felt like it was “inside a glove” and “the eye… is an absence with an immensely powerful presence.” Returning to New York after a ten-day visit to London, he therefore decided to spend the second chance of his life on just love and work. Since several Muslim entities were still celebrating his pitiable condition, he thought to make it clear to his readers that his worldview about God had not changed a bit and so he declares — “My godlessness remains intact. That isn’t going to change in this second-chance life.”
In the final section ‘Closure?’ Rushdie writes that his own anger faded, and it felt trivial when set beside the anger of the planet. He understood that three things had happened that had helped him on his journey towards coming to terms with what had happened – namely — the passage of time, the therapy, and ultimately the writing of this book. Moving along with time, he felt he was no longer certain that he wanted, or needed, to confront and address his assassin in open court and that the “Samuel Beckett moment” no longer seemed significant at all. This is where art and love overcame all barriers. He has successfully moved on and there was no need to look backwards once again.
Written a few years ago, Rushdie’s Joseph Anton: A Memoir narrated the story of how he was living a disturbed life under the pseudonym of Joseph Anton. But that memoir did not create much impact upon the readers, whereas Knife has brought back the powerful and erudite Rushdie as he has risen phoenix-like from the ashes and revealed his erudition without being parochial. Ordinary readers often shy away from his work as it is full of intertextuality and cross-references. But even those who find his writing to be too high-brow will have no problem in understanding the ‘free-associative way’ in which the mind of this writer works even today. The book is a page-turner no doubt and has brought back the popularity of Salman Rushdie once again. The simplistic yet very appealing cover of the book is an added attraction too.
Somdatta Mandal, critic and translator, is a former Professor of English from Visva-Bharati University, Santiniketan, India.
.
PLEASE NOTE: ARTICLES CAN ONLY BE REPRODUCED IN OTHER SITES WITH DUE ACKNOWLEDGEMENT TO BORDERLESS JOURNAL
Click here to access the Borderless anthology, Monalisa No Longer Smiles
Click here to access Monalisa No Longer Smiles on Kindle Amazon International