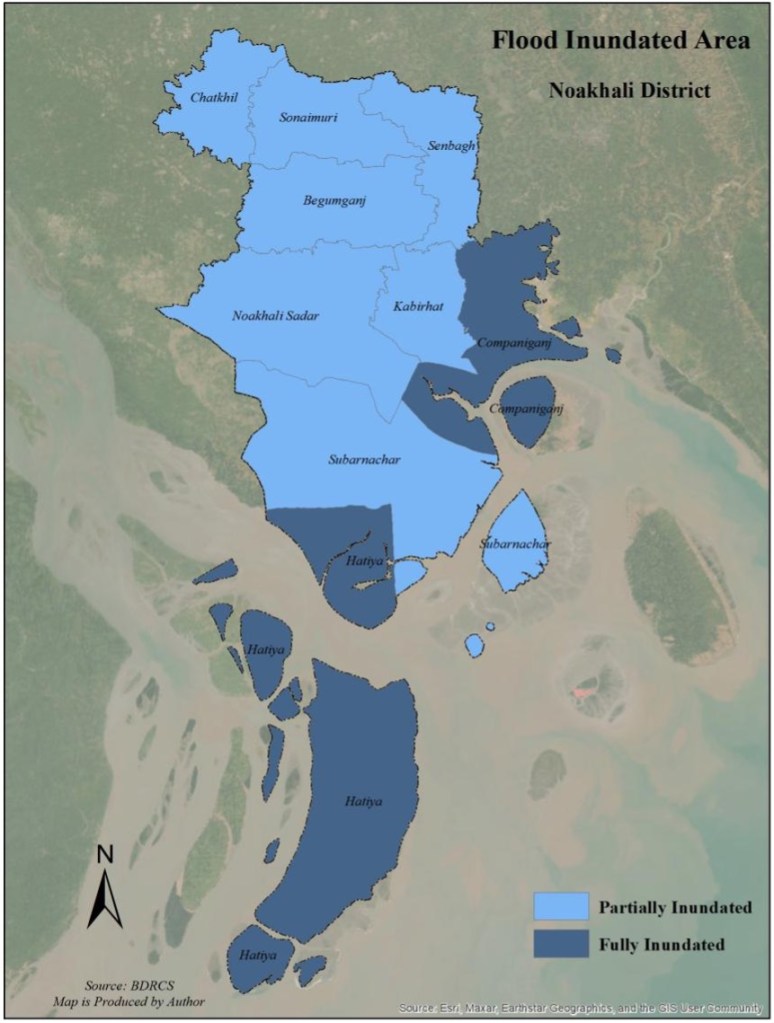
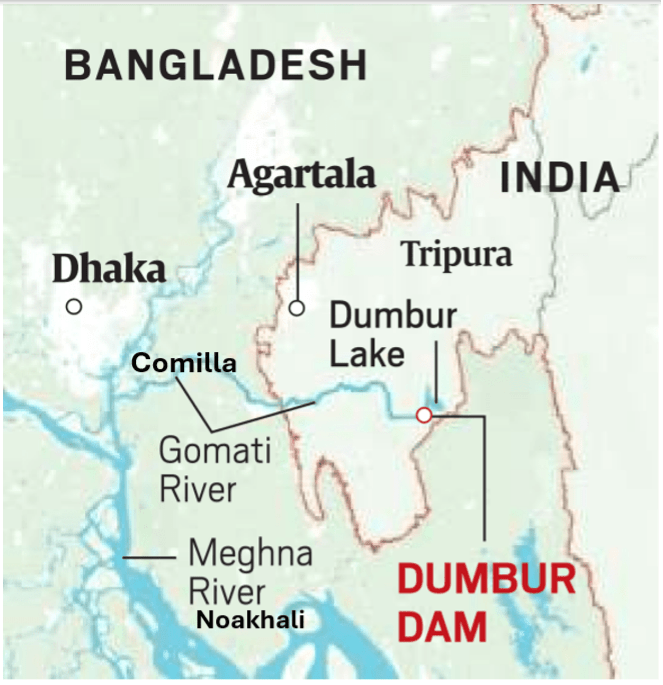
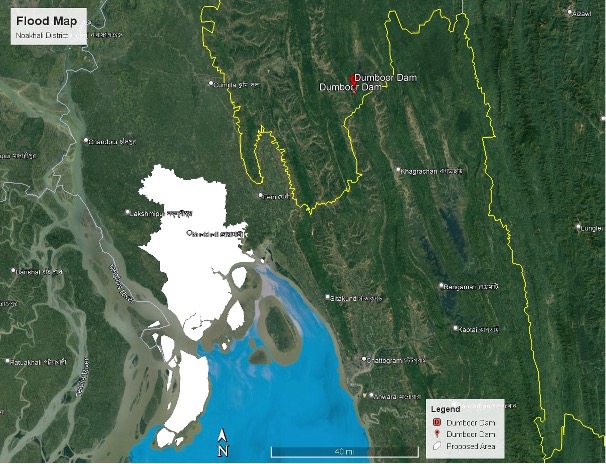
1971 began and ended on a note of hope but in the course of the year we went through the whole gamut of human emotions: love for our motherland and hate for its enemies; desire for freedom and abhorrence at those who had curtailed our right to be ourselves; feelings such as anxiety, fear, even terror caused by the knowledge that at any moment we might be abducted and murdered; and excitement and elation at the thought that relief could not be far away. 1971 was the year when for months we lived from day to day, totally insecure in a Dhaka which had become like a city of the dead; it was also the year when we discovered what it meant to hope against hope. 1971, in short, was a cataclysmal year; for every Bengali it was the year of living dangerously.
The year must have begun innocuously enough; at this point in time, I have simply no recollection what I did or how I felt in January and February of that year. But certainly, hope must have been in the air; after Sheikh Sahib’s massive election victory all of us must have been feeling confident and secure in the knowledge that we were finally about to master our destiny. For me—temperamentally apolitical and not yet out of my teens at the beginning of that year—the first sign that something was seriously wrong came one day while we were watching a test match in Dhaka Stadium on the first of March. Suddenly, the game was interrupted and then abandoned as news came about Yahya Khan’s decision to not call a meeting of the Pakistani National Assembly. Pandemonium ruled for a while in the field, but soon everyone left, muttering that this cannot be, indignant that the army chief could not go against the resounding mandate given to the Awami League to change the course of Pakistani history.
And then for a while: hartals[1], demonstrations, slogans, meetings, public displays of discontent, and the will to oppose and resist on one side and display of the carrot as well as the stick on the other. In fact, the month of March showed a whole nation in a state of ferment, ready to go to any length against a brutal but posturing force.
A first climax was Sheikh Saheb’s[2] speech of March 7. Hearing it now, I cannot but think: is it as stirring for people of this generation as it was for ours? Contemplated in retrospective, the speech seems to be the quintessence of the Bengali spirit in 1971: inspired, defiant, pulsating, and resolute. It considers the dangers ahead but is emphatic about the need to put up resistance and counter whatever measures were taken to contain us.
The real climax, of course, came on the night of March 25. That night I was in Sylhet, visiting my sister and her husband, along with my father and two other sisters. In Sylhet that night we could have no idea that Dhaka had become the scene of carnage or that our family, friends, and acquaintances were in the greatest of danger. It was only next morning, waking up to discover that Sylhet town was under curfew, and listening to Indian radio and the BBC, that we began to have an inkling of how devastated Dhaka had become in a night and in how much jeopardy our loved ones were.
Throughout the next week we alternated between a feeling of joy at the knowledge that Bengalis were fighting back and a foreboding that a grievous wound had been inflicted on us. We were elated by Major Zia’s declaration on the radio about independence and the reports of resistance everywhere; we were depressed by the news items transmitted in the air waves about Dhaka as a city that had been flattened by heavy weapons and was still burning. Since, our house was close to Farmgate, we were full of anxiety: had my mother and the sister we had left behind survived the mass slaughter of Dhakaites that was being narrated everywhere except on Radio Pakistan?
After a few days my father decided that he had had enough of waiting and uncertainty; he and I would head for Dhaka and determine for ourselves the fate of my mother and sister. My brother-in-law and three other sisters would remain in what seemed the relative safety of Sylhet. Little did we realise as we left them on a day in early April the hardship and suffering they would go through in the next few months, fleeing from tea garden to tea garden and even to the safety of Tripura[3] to escape the pillaging Pakistani army. Only after we were reunited with them in Dhaka in July did we get to know of their travails as they attempted to evade the marauding forces.
The trip to Dhaka was a tense and an unforgettable one. A few images are etched in my memory vividly: driving through the tea gardens, we saw tea garden workers with bows and arrows, determination wrought on their faces. In Brahmanbaria, we heard gripping stories of the confrontations that had taken place in Comilla and saw the intense preparations being taken in the town itself to resist the Pakistani onslaught. But the most vivid memory of the journey are the scenes of mass exodus we witnessed as we neared Dhaka: men, women, and children on foot or on rickshaws, looking harrowed, wearily fleeing to village homes from the city to escape genocide. Not a few of the people we met told us not to be so foolhardy as to return to Dhaka.
Thankfully, we managed to reach our Indira Road home without facing any unpleasant situations and found that my mother and sister were safe. But there were troop movements all the time and stories of mass arrests of young men during curfew. The elders of my family decided that I would be safer in my uncle’s house in Dhanmondi than in a house in the Farmgate area.
In the few weeks that I stayed in Dhanmondi I managed to get in touch with some of my friends. The news they told me was horrifying: Dr. Jyotirmoy Guhathakurta, my tutorial teacher, and the man who first made me feel that I had the sensitivity to be a student of Shakespeare, and who went beyond his role as a tutor to talk to me about his passion for radical humanism, as well as Mr. Rashidul Hasan, who taught us Blake and was as humble and meek as some of the denizens of The Songs of Innocence and of Experience, had been brutally murdered. More horror stories: one of my school friends, Arun Chowdhury, and his father, could no longer be traced after they had been abducted from Ranada Prasad Saha’s Narayanganj home along with the millionaire philanthropist; one of my uncle’s in-laws, a Rajshahi University professor, had also disappeared after being picked up by the army; other people that we knew had been shot at or humiliated or hurt. A friend who had joined her family in Bogra had witnessed their house being burned and the family had barely managed to escape with their lives. The whole Bengali nation appeared to be bleeding and bruised.
Nevertheless, no one felt defeated and hope still flickered as a candle newly lit and solidly fixed will even in the darkest night. For one thing, there were the daily broadcasts from Swadhin Bangla Betar Kendra[4]containing news about Mujibnagar and organised resistance all over the country. Then there was the knowledge that some friends had crossed the border and were receiving training so that they could be inducted into the Mukti Bahini[5]. Everywhere one could view the resentment against the Pakistani army being concentrated to the point when it would rebound upon them.
Eventually, my parents decided that we would take a house in a part of the city which was relatively free from regular army patrolling and I rejoined them in a Central Road flat. But, really, no part of the city was completely safe. One night, to take just one example, the boys of the neighbouring family climbed the wall separating our two houses because the army had raided the house next door and stayed with us till next morning. I still remember how tense we were that night and nervous and indignant.
Gradually, we learned to sleep better and not hear the stray shots that were fired into the night by who knows whom. Inevitably, we adapted to a life lived mostly indoors, listening to the radio or the tape recorder all day, or reading, or playing cards. But we had to be very careful about everything that we did: the radio had to be toned down, books with insidious sounding titles not read, and visit to and from friends of our age restricted. Fear of army raids constricted us and forced us to make life a diminished thing. Only my father would go out regularly to spend the day in office or shopping; his greying hair gave him a kind of limited freedom that we could not hope to have.
However, consolations for lives lived under such strained circumstances were not impossible to seek even in those days when we would rarely venture into natural light. By June, bombs which were beginning to explode at regular intervals all over the city announced loudly to us that the Bengali capacity to resist, far from being diminished, had transformed itself in spectacular fashion. My father told us one day that he was one of many people who had been donating money for freedom fighters who were now infiltrating into the city in large numbers. In July and August, the Mukti Bahini activity in Dhaka intensified and I even met a few of them. Also, every once in a while, a close friend suddenly disappeared from Dhaka and those of us who still remained in the city still unsure of what we should do talked about his decision to join the freedom struggle and his daring with a mixture of admiration and envy.
Of course, we knew that the life of a freedom fighter was far from a glamorous one, and full of risks. Exactly how hazardous their life could be was driven home to us when in late August a number of them were caught and murdered. Because we knew a few of these valiant fighters personally or by name, for some time, indeed for perhaps the only time that year, we felt depressed and shaken. But another few weeks and many amongst us roused ourselves and felt hopeful again. True, there had been a setback and some of the muktis[6]who had become legendary in a short time because of their exploits had been killed or imprisoned, but September showed that the spirit of resistance was very much alive.
Explosions could once again be heard in and around Dhaka and were signs to us of the vigour and irrepressible nature of our freedom fighters. By October, Swadhin Bangla[7]Radio broadcasts regularly reassured us that there were advances being made on the diplomatic front by our government-in-exile and that on the battlefield our reconstituted Bangladesh army were beginning to engage the Pakistani forces and defeat and demoralise them.
By early November, Nasim Mohsin, my best friend at that time, decided that it was time for him to join the freedom fighters and that the moment for a decisive assault on the Pakistani army was near. I was with him when he contacted some local muktis about crossing over to training camps in Tripura. They told him that the borders were already the site of daily skirmishes and that he should postpone the journey for a while till they could confirm a safe crossing. Desperate to become part of the freedom struggle, Nasim ignored their advice and our pleas to be patient and left us, never to be seen again. Much later, we were to discover that he had been captured by collaborators of the Pakistani army in a village in the Comilla border. They then handed him over to the local Pakistani troops who summarily shot him.
Late November and our excitement grew: the Bangladesh army was no longer content with skirmishes and raids and was now attacking the Pakistanis frontally. By late November war looked inevitable as desperate Pakistani tactics drew India into the campaign. Finally, on the night of December 3, the Dhaka night sky was spectacularly lit by tracer bullets and then invaded by Indian bombers targeting military installations. The next day all of us were on roof-tops watching dog-fights and cheering Indian jets attacking the airport and the cantonment, oblivious to the danger from shrapnel and debris from shattered planes.
Over the next two weeks, our joy grew by the hour, for every Swadhin Bangla Radio broadcast or Indian radio bulletin informed us of Pakistani reverses and detailed advances made by the liberation forces. In our enthusiasm we did not realise that we were going through dangerous times in the capital city as the Pakistani army and its collaborators, their backs against the wall, were becoming more and more vicious. It was only later that we discovered that the brother of a friend who had joined the freedom fighters had been picked up by the Pakistani army during this time and would disappear from our sights forever. And as the liberation forces closed in on Dhaka, rumours spread of youths and prominent people being abducted. Undoubtedly, the scariest memory I have from this period is of a Pakistani plane droning one night, which we knew had dropped bombs on an orphanage the previous night in a bid to discredit the Indian Air Force. It was a moment when we felt totally vulnerable and at the mercy of forces whose reason had become warped to the extent that they could indulge in mass destruction of innocents merely to smear India in the eyes of the world.
Nothing the vicious Pakistani military/propaganda machine could do, however, could thwart the logic of history and prevent liberation, and by December 15 we were hearing the booming of artillery in and around Dhaka. On December 16, we headed for the Ramna Race Course area because we heard that a surrender ceremony was scheduled there in the afternoon.
But we could only go as far as the Hotel InterContinental, where we got caught in a cross-fire. A friend who was with me got slightly hurt as a splinter from a bullet pierced his leg. We took him to his house and then scattered, telling ourselves that we had not survived nine months of occupation only to get killed at the moment of liberation. But by evening we were out in the streets celebrating with muktis, among whom I could see at least one close friend, firing his Sten gun into the air. The year of living dangerously was ending, and the time for unmitigated hope had finally come to stay with us, at least for a while!
(Published on March 31, 2019, The Daily Observer)
[1] Strikes
[2] Sheikh Mujibur Rahman (1920-1975)
[3] A northeastern state of India
[4] Independent Bengali Wireless Centre
[5] The freedom vehicle: The army that fought to free Bangladesh as an independent entity
[6] Freedom fighters
[7] Free Bengal
Fakrul Alam is an academic, translator and writer from Bangladesh. He has translated works of Jibonananda Das and Rabindranath Tagore into English and is the recipient of Bangla Academy Literary Award (2012) for translation and SAARC Literary Award (2012).
PLEASE NOTE: ARTICLES CAN ONLY BE REPRODUCED IN OTHER SITES WITH DUE ACKNOWLEDGEMENT TO BORDERLESS JOURNAL
Click here to access the Borderless anthology, Monalisa No Longer Smiles
Click here to access Monalisa No Longer Smiles on Amazon International