By Paul Mirabile
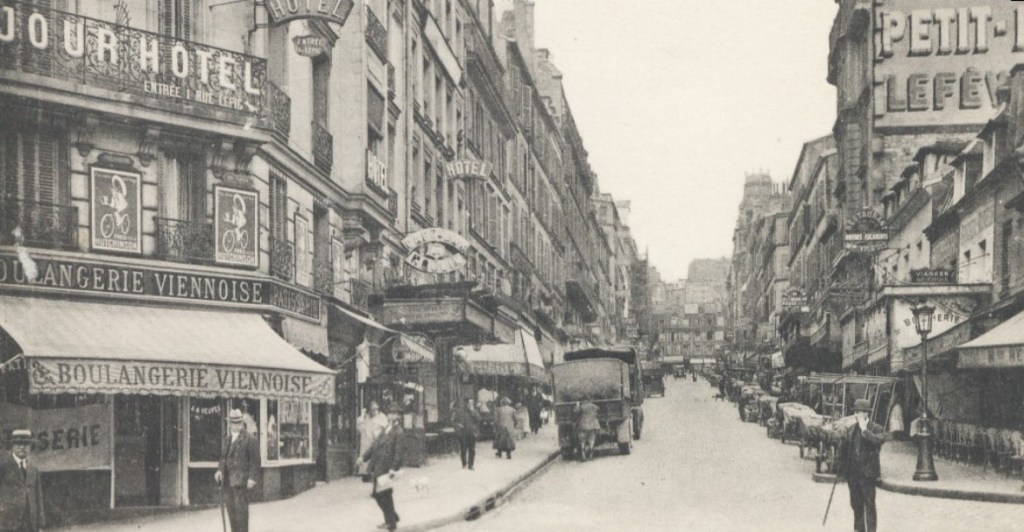

In 1974, the modest, starless Hotel du Commerce, at 14, Rue[1] Sainte Geneviève, in Paris became my home for over six months, and its owner, Madame Marie, my adopted mother.
A young, aspiring journalist, I was sent to Paris by the editor of a worthless monthly magazine in Palermo, Sicily, to write an article on the monuments of Paris. I took up my long residence at the Hotel du Commerce for two reasons: it was very cheap — that is, ten francs a day — and conveniently located in the centre of the city, only a ten minute walk to the Notre-Dame Cathedral. Madame Marie, ninety kilos of joy and laughter, rented me a room on the fifth floor (without a lift) with two other residents: Caban across from me and Paco at the end of the corridor. The rooms had neither attached toilets – there was one for each floor — nor showers (none). Like all residents and tourists, we washed from the washbasin in our rooms. My little window looked out on to the red-tiled rooftop of a Russian bookshop.
To tell the truth I never wrote that article on the monuments of Paris. What a boring subject! On the other hand, my stay at Madame Marie’s hotel afforded me enough material to write a book — a sketch of her and her residents, their trades, joys and sorrows … their uncelebrated destinies. My editor would have probably sacked me for this ‘breach of contract’, but as luck would have it, his magazine went out of business before my return to Palermo.
I shall never know why Madame Marie took such a liking to me. Everyday, she would invite me for coffee and a chat. We would even watch television in the evenings in her sitting-room which separated the tiny kitchen from the reception. From there she kept an alert eye on the comings and goings of everyone. She was a jolly old woman, and this, despite the loss of her husband at an early age, and the terrible events that occurred in her hotel during the Algerian war in the fifties and sixties[2]. She was indeed fat, but quick-witted with plenty of pluck. She had rolls of flesh rumbling under her eye-catching flower-dotted red robe.
“You know, I was a young girl during the Second World War. I hid some French Resistance fighters in my parents’ house in the Alps. The Germans who hunted down the French fighters couldn’t scare me with their rifles and threats. I sent them packing whenever they pounded at our door!” she would repeat proudly when I was alone with her. When her husband died, she was left on her own to manage the hotel, and in the 50’s that was no asset. Deserters, police informers, merciless OAS members[3] and their equally ruthless adversaries, the FNL[4] all came and went causing rows, arrests, even murders. The plucky Madame Marie handled it all with her sang-froid and flair for compromise.
“My sixth-sense got me through that lot,” she would laugh, her jowls shaking. By the 1970’s, however, things had calmed down in Paris. The lodgers were mostly Japanese and American tourists with a sprinkling of North Europeans. No more brawls, police raids or murders. Madame Marie spoke no foreign language but she understood everything that she needed to understand. She had hired an old woman to clean the rooms. The sprightly widow had learned how to say in English, after having knocked on the lodger’s door at eight in the morning: “You stay or you go?” It was enough to get her point across.
Madame Marie disliked the police. She flared at their scent even before they stepped through the front door in incognito on the trail of someone except on one occasion. I shall let her narrate that exceptional episode: “How that flic[5] fooled me I’ll never forget. Dressed like a hippy, long hair, a torn knapsack, he took a room in the courtyard. He spent two weeks here and never said a word. He got in no later than eight o’clock at night. I thought he played the guitar on the metro[6] for money. Then one day, dozens of police stormed through the front door into the courtyard. I was in the sitting-room and rushed out the back door of the kitchen to see what all the hullabaloo was about. The door of one of my clients was wide open, a young bloke who used to play the guitar on the metro; he had been handcuffed by the ‘hippy’ and was being walked out. I couldn’t believe it. It was like a film. When everything settled down, a police officer came over to me and politely explained that my lodger was a notorious drug-dealer and had been under surveillance for weeks by the ‘hippy’. He apologised for the inconvenience and paid the rent for both the dealer (who hadn’t paid me) and the hippy-policeman.” Madame Marie sighed. “He’s the only flic who ever fooled me.” And she laughed her usual jolly laugh.
She got up to make some more coffee for at that moment Caban and Bebert came in for a chat, both a bit tipsy from their usual drinking bouts before, during and after work. Then Bebette made her appearance, the prostitute to whom Madame Marie ‘lent’ one of the courtyard rooms every now and then to exercise her profession. Madame Marie had no moral qualms about such professions. Everyone had to earn a living … Close behind sailed in an elderly woman whose name I no longer recall. Madame Marie considered the woman to be her best friend. She would sit in front of the television and shout insults at the politicians whom she disliked, much to the displeasure of the others, especially Bebert, who would shower her with mocking abuse. When things got too rowdy Madame Marie would shout them all down or threaten to turn them out if they didn’t settle down.
Madame Marie was at times brusque but fair. She liked Caban, the former butcher and now factory worker hailing from southern France, shy and lonely, drunk by mid-morning. He had been living in Hotel du Commerce since the late sixties. She was fond too, of Bebert, the chimney-sweep, a small, taciturn, melancholic chap straight out of Dicken’s David Copperfield, drunk before ten in the morning. He constantly coughed. His clothes were impregnated with soot and cigarette smoke. Bebert hardly spoke at the table, smoking like a chimney, drinking his coffee whilst Caban smiled and winced at the others’ ridiculous jokes and jibes. Day after day and night after night that sitting-room typified for me – and for the others, I suppose — a sanctuary of friendship and convivial exchange. Oftentimes, I read myself into a page of Balzac’s novel Le Père Goriot [7].
The other two residents rarely joined at that cheery table. One of them, Bolot, stayed in a room in the courtyard. He was a former German soldier who joined the French Foreign Legion after his capture during World War II. The other was called Paco, a Republican Spaniard, who escaped Franco’s persecutions after the Spanish Civil War[8].
I got to know them all, save Bebert. We had no time to get really acquainted. “Poor Bebert,” Madame Marie would sigh. One evening as we sat watching a film Bebert knocked at her kitchen door, then staggered in towards us, blood streaming from his mouth, drenching his night-shirt. His face was ghost white. He kept murmuring, “Madame Marie … Madame Marie,” through clenched, blood-filled teeth. The chimney-sweep appeared lost in a daze. Madame Marie quickly took him by the shoulders, laid him on the sofa then trotted off to get the police. They arrived quickly (the station was two doors away). An ambulance shortly followed. Bebert was placed carefully on a stretcher and carried out.
We never saw Bebert again nor had any news of him. Madame Marie presumed that he had died of a haemorrhage from too much smoking, drinking and chimney soot. She had his room cleaned and fumigated. His belongings amounted to a pair of torn slippers, two shirts and trousers and two used razor blades. On the other hand, she gasped at the hundreds of empty packs of cigarettes. Bebert’s world had been compressed into a nebulous routine of cigarette and alcohol fumes and chimney soot. A bleak, Dickensian world to say the least.
Poor Bebert. He had been living at Hotel du Commerce for eleven years. A fellow without a family, friends … known to no one. He practiced a trade that was gradually dying out. No one ever asked for him at the reception — never a phone call. He was the unknown toiler whose burial stone carries no name because he had no money for a headstone. He was probably buried in the fosse commune[9].
Caban, whom I knew much better than Bebert, fared no better. His salary flowed away upon the torrent of fumes of cigarettes and drink, or as Madame Marie put it coarsely: “He pissed it all against a wall!” Too much gambling, too. So his wife left him, after that, his sixteen-year-old daughter. They were never to be heard from again. Caban was soft-spoken, very shy. Quite frankly, I never saw Caban sober, except at six in the morning before catching the bus to work at the wine-bottling factory. He had asked the foreman, Mister Tomas, to have me hired on for the summer since many of the workers had gone off on holiday. In the café whilst waiting for the morning bus, he began his inglorious day with coffee and a few shots of cognac. He continued his indulging all through the working day on the first floor of the factory where he drank the last dregs of wine from the bottles that were to be washed. By five o’clock he was completely sloshed! Mister Tomas kept him on out of pity. Besides, Caban was inoffensive. Madame Marie even told me he had saved a girl from drowning in the Seine River in Paris. But let Madame Marie tell this very true tale: “He was walking along the banks of the Seine after work when he heard the screams and splashings below him. Caban was a strong swimmer at that time, so he took off his shoes, dived in and grabbed the girl in the water. In a few minutes he had brought her back to the banks safe and sound where a crowd of people had gathered, applauding him. The young girl cried and cried but was unhurt. And you know, her father was the owner of the France-Soir daily newspaper. So, to thank Caban, he gave him a certain sum of money and offered him the France-Soir freeeveryday for the rest of his life. All he had to do was give his name at the news-stands.”
“Does Caban read the France-Soir? I never see him reading a newspaper,” I asked naively.
She laughed. “No, Caban never reads. He never had much instruction.”
I became quite friendly with Caban since we worked together at the factory, although he would constantly upbraid me for not joining him in his ritualised morning concoction. I insisted that I never drink. He would snicker and shrug his bony shoulders. “All men drink!” he slurred. That of course was a subject of conjecture which, and this goes without saying, I never pursued with him.
One day whilst I translated for Madame Marie at the reception, I mentioned that I hadn’t seen Caban for more than a week. Neither had she. Mister Tomas had telephoned, too. Caban never missed a day at work … never. She told me to go upstairs and knock at his door. Which I did for several minutes. Silence. When I returned without news of him she immediately dawdled out to the police station. She was back in no time with two policemen. I accompanied them upstairs. They pounded at the door then kicked it open. There knelt Caban over his bed, his face black as coal. The stench in his room made us gag. I hurried down to tell Madame Marie. And as we stood in the reception, the ambulance arrived and four men, escorted by the police, placed Caban’s frail, limp body into a plastic bag and dragged it down the steps, one by one : thump … thump … thump … Madame Marie started to cry. I covered my ears …
Poor Caban had been dead for over a week, due no doubt to a blood clot of the brain. Madame Marie never forgot those thumps on the flight of stairs. Nothing was said of his death in the newspapers, even in the tabloids. Like Bebert, he succumbed to a companionless death, without flowers or prayers. Without sorrow or tears … He too was probably buried in a fosse commune. He had no bank account. The police found six Francs in his pocket … Six more than in Bebert’s …
Paco, the Spanish refugee, had been living in Hotel du Commerce for seven years. His lack of good French isolated him from the Paris scene, so he took refuge in the clusters of Hispanic scenes that peppered the Parisian streets, especially the taverns where flamenco music could be heard on Rue Moufftard, only a fifteen-minute walk from our hotel.
Since I speak Spanish quite well, I had on many occasions accompanied Paco to these musical haunts of his, where the paella was copious, the sangria flowed like water, the music, if not excellent, loud enough to forget one’s trials and tribulations of the day. Above all, it was cheap …
Paco drank heavily, rum and coke or sangria, but never behaved uncivilly. His deep, black eyes bore into mine whenever he spoke of his luckless past: “My older brother was killed in the war against Franco. I escaped via the Pyrenees leaving behind my parents. Since 1940, I’ve been living in France, working in factories or in the fields. And you know, I still don’t have my French papers. I have no identity! I can’t go back to Spain because of Franco[10], so I must stay here unloading lorries at the Halle Market or washing dishes in grotty gargotes [11].” Paco clapped to the sound of tapping feet and to the rhythmic chords of a furious guitar. “Every now and then I repair the toilets at the hotel which are constantly clogged up.” He snapped his fingers, ordered tapas[12], spoke to his friends in the language of his parents.
The fiery Spaniard would introduce me to his Spanish artist friends, all of them sullen, sad figures whose love of Spain had evaporated into hazy fumes of sangria, nostalgia, gaudy flamenco music, tasteless tapas and brief love affairs. As to Paco, he appeared to be a loner, an ill-starred chap lost in a huge city of lost souls, of crowds so busy that their business took no heed of such a shadowy figure, fugitive and fleeting, drifting from tapas to tapas, sangria to sangria.
Paco hated Paris, but it proved the only place for a stateless refugee to avoid police roundups. For Paco, Hotel du Commerce symbolised a haven for marginals, the homeless and stateless. “Madame Marie is my guardian angel,” he would croak. “My very fat guardian angel” as he clapped and stamped to the riotous music. “The police will never find me … never!” he boasted raising his glass to Madame Marie’s health.
He was wrong. One hot September week, Paco couldn’t be found in the hotel. Madame Marie suspected foul play. Two days later the police arrived, informing her that a certain Paco Fuentes had been apprehended without papers. He had been extradited to his country of origin. His belongings? He had none, like Bebert and Caban. The little he did possess were thrown into a bag and out into a rubbish bin. Poor Paco — would he ever find his parents?
On my many jaunts through Spain, after Franco’s death, I tried to locate Paco Fuentes, but it was like finding a needle in a haystack as the expression goes. Here, however, I must thank the excellent Spaniard, for it was he who introduced me to the world of flamenco.
Bolot kept very much to himself. Unlike the other residents he never drank nor smoked. You didn’t want to muck about with Bolot — a massive fellow, indeed. But then again who would muck about with a former French Foreign Legion soldier?
Yet, Bolot’s aloofness and reserved demeanour attracted many people to him. He had that sort of winning smile, and since he spoke very good French, albeit with a heavy German accent, he befriended those who came into contact with him. Moreover, he shared a passion for stamp-collecting. That was Bolot’s raison d’être[13]! His collection had become very well known to both specialists and amateurs. I would accompany him to the Flea Market on Sundays and there he would trade stamps with the best of stamp-collectors. Stamps from the Soviet Union, China, India, Cuba, several African states, Turkey and Libya. Bolot didn’t need the money, his pension as a soldier was comfortable enough. He simply enjoyed the thrills.
One day as we strolled back to the metro as he towered above me, Bolot acknowledged his good luck: “I volunteered for the army at seventeen, an enthusiastic patriot. Was captured by the French after two days of combat and given a choice: prison or the Foreign Legion. I chose the second, changed my nationality and name.”
“What was your German name?” He smiled but left the question unanswered.
“So I fought for the French. A traitor to my homeland. Call me what you like, I couldn’t sit out the war in a prison for years and years. You know, I never went back to Germany. When I quit the Legion I received my pension and came straight to Paris, the City of Lights.”
“To do what?”
“To sell stamps!” Bolot laughed. “No, I worked as a mechanic in factories until retiring.”
I got to know Bolot as well as Caban since all three of us worked at the same wine-bottling factory in the summer of 1974. He left earlier than me because of a fight between him and an obnoxious individual who abhorred Germans, even though Bolot had acquired French nationality long ago. Bolot refused to fight him, despite the other’s punches, which the former Legionnaire dodged or blocked with considerable ease. If Bolot had really fought, he would have killed him. Mister Tomas broke up the squabble, sacked the young rowdy on the spot and apologised to Bolot. Bolot exercised the noble art of self-restraint.
When I left for grape-picking at the end of September, then on to Italy and Sicily, it was Bolot who helped me repair the broken spokes of my bicycle. Outside Hotel du Commerce, Madame Marie and Bolot wished me the best of luck, inviting me back whenever it suited me. There would always be a spare room for me she insisted. I cycled out of Paris in the direction of Burgundy. I had spent six months at Hotel du Commerce …
After a month of grape-picking I returned to Palermo only to discover that the magazine had failed due to lack of interest … and funds. Relieved, I went to Madrid to begin a career as a flamenco guitarist. Time passed quickly. Or as Madame Marie would philosophically say: “It’s not time that passes but us!” Exhausted from so much playing in studios and taverns, I decided to take a break and travel to France and visit Hotel du Commerce.
It was under new ownership. The manager, an Italian, informed me that Madame Marie had died years ago from dementia after a spell in a nursing home. How everything had changed: the reception room had been refurbished and Madame Marie’s Balzacian sitting-room had become a dining-room for guests. The once starless hotel had become a three-star hotel.
I stayed two nights and paid sixty euros a night! In the seventies, I paid the equivalent of one and a half euros! True, all the rooms had been painted in bright, cheery colours, fitted out with toilets and showers. But sixty euros? Besides, I like a hotel that is lived in, not just slept in …
With the death of Madame Marie, a whole era had come to a close. Hotel du Commerce had decidedly conformed to the standards of kitsch. There were no more residents, only tourists. All the single rooms on the fifth floor had become large rooms suitable for modern travelling couples. Gone were the days and nights round Madame Marie’s convivial table, her coffees and conversation. Those colourful figures who had imprinted their existence there, whose joys and sorrows had been shared by Madame Marie and myself, no longer painted those refurbished walls simply because the epoch ignored the very existence of such figures.
Indeed, who during those two nights reminisced the glittering epoch of Madame Marie’s Hotel du Commerce? Who even imagined her singular story and those of her likeable, touching residents? No one. No one, perhaps, except me, who vouched to safeguard those memories. Memories of the anonymous whose faces will never be seen on photos, nor names ever printed in books.
[1] ‘Street’.
[2] 1954-1962.
[3] ‘Secret Army Organisation’ founded in 1954 that fought against those forces who wished to prevent the independance of Algeria.
[4] ‘The National Liberation Front’, also founded in 1954 whose militants fought for the independance of Algeria.
[5] Jargon in French for ‘policeman.
[6] ‘Underground’ or ‘subway’.
[7] ‘Father Goriot’ written in 1834. Translated into English by Ellen Marriage.
[8] 1936-1939.
[9] ‘Communal grave’.
[10] General Francesco Franco died in 1975, and with his death, King Juan Carlos proclamed Spain a democratic nation.
[11] French jargon for ‘cheap, unsavoury restaurants’.
[12] Spanish appetisers.
[13] French: Reason for being
.
Paul Mirabile is a retired professor of philology now living in France. He has published mostly academic works centred on philology, history, pedagogy and religion. He has also published stories of his travels throughout Asia, where he spent thirty years.
.
PLEASE NOTE: ARTICLES CAN ONLY BE REPRODUCED IN OTHER SITES WITH DUE ACKNOWLEDGEMENT TO BORDERLESS JOURNAL
Click here to access the Borderless anthology, Monalisa No Longer Smiles
Click here to access Monalisa No Longer Smiles on Kindle Amazon International