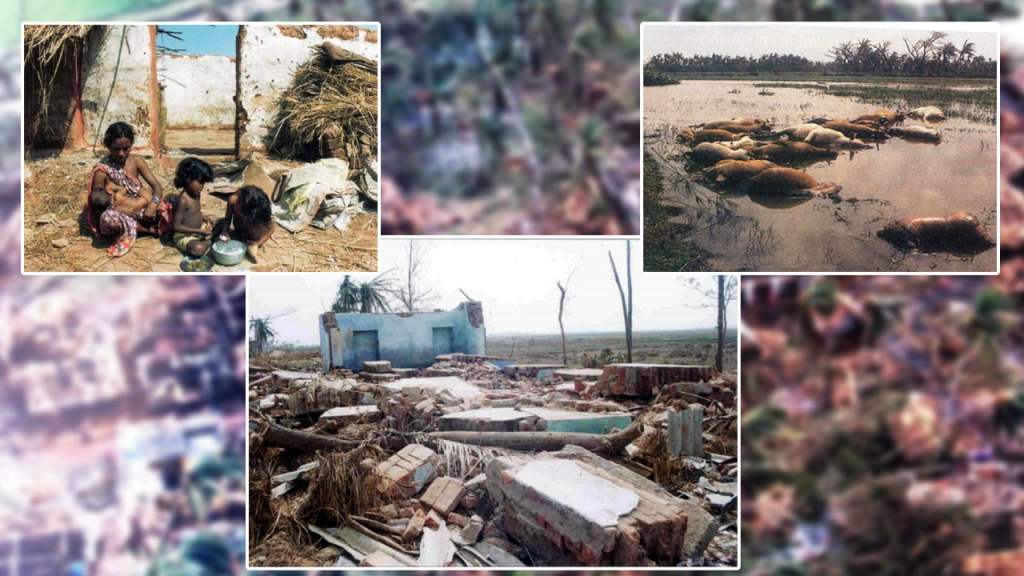
Zeeshan Nasir writes of a region whose carbon footprint is next to zero, yet it suffers some of the worst climate-related disasters…


The perennial consequence of climate change is affecting the lives of people all over the world, particularly in the remote and underprivileged parts of Balochistan.
Noora Ali, 14, was oblivious to the temperature shifts because she had grown up in Turbat, a city in the centre of CPEC (China-Pakistan Economic Corridor). They had frequent floods during the monsoon season and blazing heatwaves during summers, with temperatures rising above 51 centigrade. Compared to other cities in Balochistan, Turbat experiences hot summers and typical winters. As a result, the majority of wealthy families in the city travel to Gwadar, Quetta, or Karachi during the sweltering summers and return to Turbat during the winters. The Water and Power Development Authority (WAPDA) moved Noora’s father, who works there, to the neighbouring Gwadar in 2022.
In the February of 2022, the sea seemed calm while boats of the fishermen busily dotted the waters of the Padi Zir (Gwadar’s West Bay). It was a typical Thursday morning when rain started pouring down. The rain was so intense that the sea became wild and uncontrollable. The roads were washed away, bridges collapsed, with streets being inundated with flood water and the port city became completely disconnected with the rest of the country. Back in Turbat, her ancestral hometown was also submerged under flood water.
Noora had also heard from her school fellows that Gwadar and Turbat had never experienced such heavy and intense rainfall before. She knew and felt that the temperature of her native city was rising and that Gwadar beneath flood water didn’t seem normal. “This is due to climate change.” Her elder brother told her. At the age of 14, typical children in Balochistan have no idea what climate change and global warming are but they are already feeling it impacts.
Like Noora, thousands of children in South Asia, particularly Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal, India and Afghanistan are at the risk of climate related disasters, as per the UNICEF 2021 Children’s Climate Risk Index. The report further reiterates that children in these countries have vigorously been exposed to devastating air pollution and aggressive heatwaves, with 6 million children confronting implacable floods that lashed across these countries in the July of 2024.
On the 11th and 22nd November 2024, over 20 youths urged the world leaders to come up with plans to mitigate the impacts of climate change on children at the 2024 United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP 29) held in Baku, Azerbaijan. Among those 20 resolute children was the 14 years old, Zunaira Qayyum Baloch representing the 241.5 million children and women of Pakistan.
Dressed in her traditional Balochi attire, with a radiant smile in her face and resolute in her commitment, Zunaira Qayyum Baloch, startled everyone. Hailing from the far-flung district of Hub in the Southwest of the Pakistan’s Balochistan, Ms. Baloch went to represent the children of a country whose carbon footprint is next to zero, yet it suffers some of the worst climate-related disasters. Her message to world leaders was clear: step up and combat climate-induced inequalities, particularly those affecting women and children.
She had always remained conscious about the changing climate in her city, observing the floods of 2022 that had wreaked havoc in Hub Chowki, initiating awareness programmes and youth advocacy guide training in her home city to advocate for girls right to education and climate change.
“After my father passed away, my mother became the sole breadwinner. She helped us get an education and met all our requirements.” Zunaira explains. “During the catastrophic rains of 2022, an incident changed my perspective on climate change. Rainwater had accumulated in the roof of our home and streets were flooded with water. The destruction was so overwhelming that I realised that such events were no longer rare but increasing constantly. “
During the COP29, Ms Baloch expressed her concerns with the experts how Pakistan, particularly Balochistan has been detrimentally affected by climate disasters like frequented floods, heatwaves, hurricanes and droughts. Lamenting that climate change was a child-rights crisis, she told the world how the changes in the climate had jeopardised the lives of millions of women and children throughout the world.
Asking the world leaders to join determined children like her to combat climate change, she addressed them in the COP29: “Climate change matters to me, and it should matter to you too.”
Stark Reality of the Past
Bibi Dureen, 80, is a testimony to how climate is continuously transforming. She hails from the outskirts of the Kech district in a town called Nasirabad.
“The seasons are changing.” She says with her voice laced with sorrow. “The heatwaves have become more aggressive, and floods are common. It all started around 1998 in Turbat. Then in 2007, a devastating flood destroyed our homes, date palm trees, livestock –and worst of all, it took lives.” She pauses, her wrinkled hands trembling.
As she talks to me in front of her thatched cottage, through which sunlight is streaming in, tears well up in her eyes as she recalls a painful childhood memory, “I was young at that time. It was a pitch-black night, and the rain was pouring down mercilessly when a man came shouting that the flood water had reached the fields.” She exclaims with grief. “My mother, desperate to save what little we had, sent her only son, my sixteen-year-old brother, Habib, our family’s only breadwinner, to find the only cow we had in the fields. Neither the cow nor Habib returned. Later some men found his dead body in the jungle.”
In June 2007, when the Cyclone Yemyin hit the coast of Balochistan, it wrought unprecedented damage to the province, particularly Turbat, Pasni and Ormara and rendered 50,000 homeless within 24 hours, including children. According to reports 800,000 were affected and 24 went missing.
The 2022 floods had a devastating impact across Pakistan, with the province of Balochistan being one of the hardest hit. With 528 children dying nationwide, 336 people died in Balochistan, including children as per the reports of the Provincial Disaster Management Authority (PDMA).
Tragedy struck again in 2024 when torrential rains engulfed 32 districts of Balochistan, particularly, the port city of Gwadar and Kech district. The PDMA put the death toll of children dying due to the flood at 55 out of the total of 170, with 16 others injured.
The Double Crisis Facing Girls
Regions in Balochistan, such as Naseerabad, Jaffarabad, Sohbatpur, Nokundi, Sibi and Turbat have seen severe heatwaves in the past few decades. On May, 2017, the Mercury rose to a record breaking of 53.5 centigrade in Turbat, making the district to be the hottest place of the year after Mitribah, Kuwait. During heatwaves, cases of fainting and health-related illness among residents, particularly children are rarely uncommon. According to a 2023 report by the Pakistan Meteorological Department, Balochistan has seen a 1.8°C rise in average temperature over the past three decades, leading to longer and harsher heatwaves.
Dr Sammi Parvaz, a gynaecologist at the university hospital in Turbat, tells that rising temperatures in the district not only contribute to higher dropout rates among school-girls but their menstrual cycle is also affected.
“According to the recent research of the National Institute of Health (NIH) , menstruation– a biological process that occurs in females when they reach puberty — is severely affected in countries which are vulnerable to climate change and Pakistan is one them.” She explains. “The menstruation in girl children living in extreme heat, such as, in Turbat and Karachi, becomes very intense, painful and with cramps.”
Dr Sammi further elaborates that this phenomenon is linked to the increased release of cortisol and oestrogen, the hormones which regulate the female reproductive cycle. “Girl children exposed to harsher environments such as severe heat or cold, experience hormonal imbalances leading to irregular periods and severe menstrual cramps. The hospitals in Turbat are frequented by patients suffering from intense cramps or irregular periods.”
Hygiene becomes another pressing issue during floods, especially for young girls. Research published by the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health states that floodwater contains lead, polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and other chemicals which are the cause for irregular periods.
During floods thousands of girl children struggle to manage their periods amidst the chaos of the disaster and remain without period products. For instance, after the 2022 floods, 650,000 pregnant women and girl children in Pakistan were without essential maternal care, with a significant proportion from Balochistan.
Admist all this chaos climate activist like Zunaira Qayyum Baloch raise awareness while women like Maryam Jamali work directly on the ground to ensure that every women has ration in her house and access to menstruation products during catastrophes.
Madat Balochistan [1]— a non-profit organisation — has supported more than 31,000 people across 34 districts in Sindh and Balochistan. With its major work concentrated in and around Quetta, Dera Bugti, Jaffarabad, Jhal Magsi, Sohbatpur, and Khuzdar, they are a women-led organisation fundamentally prioritising women and young girls in their work because even on the frontlines, they are bearing most of the cost of climate change, according to its co-founder, Maryam Jamali.
“Our conversations on climate change vulnerability often treat everyone as ‘equal’ in terms of impact, when that is far from the truth. Vulnerability is a multi-dimensional concept and in a country like Pakistan where most of the women and girls are pushed to the margins of society in every way possible — we cannot just overlook their struggles.” Maryam Jamali tells.
“Take the 2022 floods, for example — the most recent catastrophes etched in our memories. Women and girls were responsible for most of the labour when it came to evacuating to safer places. As soon as they did, their needs when it came to menstruation or pregnancy care were completely ignored by aid agencies as they sent out packages or set up medical camps. Most of our work at Madat was compensating for things like this. We worked with midwives to ensure that women, who could not stand in lines for ration, received it regardless or women who did not want to interact with male doctors didn’t have to. In our housing projects, we prioritise women especially those who don’t have a patriarch in the household because that severely limits their access to resources for rehabilitation.”
Floods, heatwaves and other natural calamities are gender neutral. However, female children are more likely to be affected by them. According to the UN Assistant Secretary-General Asako Okai that when disaster strikes, women and children are 14 times more likely to die than men. In Pakistan, 80% of people displaced by climate disasters are women and children.
In patriarchal societies in Pakistan, women and female children are the primary caregivers of the family and they are the sole persons to grow crop, do house chores, fetch firewood and water. With little to no potable water nearby, girls have to travel far to help their parents, further exacerbating their vulnerability.
These household responsibilities create an educational gap. Girls are taken out of schools in Balochistan during floods. With Pakistan’s lowest girl literacy rate at just 27 per cent, the International Rescue Committee (IRC) reported that the province of Sindh and Balochistan have seen greater educational disruptions due to heatwaves and floods, with the 2022 flood causing more educational institutions closure than the combined two-year COVID-19 pandemic.
Extreme heatwaves and recurrent flooding in Balochistan have further compounded this gap. For instance, the 2022 flood damaged or destroyed 7,439 schools in the province, affecting the education of over 386,600 students and 17,660 teachers and staff members. Reports also mention that most of the government school were used as flood shelters in the province. In the 2024 floods, 464 schools were again damaged.
The destruction of educational infrastructure has forced many children out of school, contributing to the province’s high out-of-school rate.
Monsoon Brides during Floods
Though floodwater is no longer accumulating in the Mulla Band Ward of Gwadar district in Balochistan, the damage it has wrought will stay with the people for a long time for many years. For Gul Naz[2],16, the loss has been devastating.She was only 16 years at the time when flood water entered their home in 2022. Her father, being a fisherman, struggled to make ends meet, as the sea was completely closed for fishing, cutting off the family’s only source of income.
“I was in the Jannat Market and when I returned home, I was told by my mother that my marriage has been fixed to a man twice my age in exchange for money.” She discloses that her parents were given Rs.50,000 ($178.50) which is a whooping sum for a poor family, who survive on around one dollar a day.
“I have two kids now and I am a child raising a child.”
The sadness in Gul Naz’s voice is palpable and she isn’t alone in her predicament. During floods and emergency situations, families in Balochistan resort to any desperate means for survival. The first and most obvious way is to give their daughters away in marriage for financial relief — a practice that usually surges during the monsoon season, hence, the name monsoon brides.
In the Sindh province of Pakistan, where this trend is more prevalent, there has been a spike in the number of monsoon brides during the last flash floods of 2022. In the Khan Mohammad Mallah Village, Dadu district, approximately 45 were married off in that year, according to the NGO organisation, Sujag Sansar[3], which works to reduce child marriages in the region.
Pakistan stands at the sixth position in the world when it comes to marrying children below eighteen. While there has been a reduction in child marriages in Pakistan in recent years, UNICEF warns that extreme weather patterns put the girl child at risk.
Madat Balochistan has also been on the forefront in the reduction of child marriages in Balochistan, “It’s not intuitive to think of girls’ education or loan relief or housing provision as measures to build climate change resilience, but in our contexts, these are the very things that drive vulnerability to climate change.” Says the Maryam Jamali. “We have been working on supporting farmers with loan relief so that young girls aren’t married off to compensate for the financial burden of loans after a lost harvest. We are also working on initiatives for sustainable livelihoods for women as well as ensuring that young girls in all the communities we work in have access to education despite geographic or financial limitations.”
Jamali thinks that gender inequality is one of the biggest aspects here which makes it absolutely necessary for a region like Balochistan, where physical vulnerability and socio-economic vulnerability is high, to have young girls at the decision-making table.
“Activists like Zunaira can ensure that when we come up with solutions for climate change, we contextualize them through a gender lens and make sure that this does not become another instance of taking away women’s agency but becomes an opportunity to involve them in climate change policy decision-making.” Jamali contends. “It is rewarding to see the girls we support do great things. One of our girls from Musakhel is studying at Cadet College Quetta, the first in her family to be able to pursue education beyond 8th grade.”
The Way Forward
“Extreme weather can fuel conflict and be a threat multiplier,” says Siraj Gul, a lawyer at the Balochistan High Court, Quetta, citing the recent research published in the journal Alternatives: Global, Local, Political. He stresses that the decades long running insurgency in Balochistan stems from human rights violations, inequality and government negligence. “Climate related catastrophes further destabilise the region’s development. For instance, there was a surge in the number of protests during the 2022 floods in Gwadar, Lasbela and Turbat, reflecting the deep frustration and despair of the people.” According to Mr. Gul if children like Zunaira are given a platform to speak and work for Balochistan, they are not merely advocating for the environment, they are working for a more peaceful and tranquil region.
A climate resilient infrastructure and child-oriented disaster relief have become a must in climate-torn regions like Balochistan.
[1] Help Balochistan
[2]Her name has been changed to retain her privacy
[3] Awake World
Zeeshan Nasir is a Turbat-based writer and currently pursuing his MBBS Degree from the Makran Medical college, Turbat. He tweets on X @zeeshannasir972. He has contributed to Daily Dawn, Countercurrents, Pakistan Today, The Diplomat and others. A different version of this essay has been published earlier in Countercurrents and Pakistan Today.
.
PLEASE NOTE: ARTICLES CAN ONLY BE REPRODUCED IN OTHER SITES WITH DUE ACKNOWLEDGEMENT TO BORDERLESS JOURNAL
Click here to access the Borderless anthology, Monalisa No Longer Smiles
Click here to access Monalisa No Longer Smiles on Amazon International